Popcorn is a beloved snack enjoyed by many, often prepared in the convenience of a microwave oven. But have you ever wondered what happens on a scientific level when popcorn pops? Specifically, is this process endothermic or exothermic? In this article, we’ll dive into the science behind popcorn popping in a microwave, unraveling whether this phenomenon is an endothermic or exothermic reaction.
Understanding Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
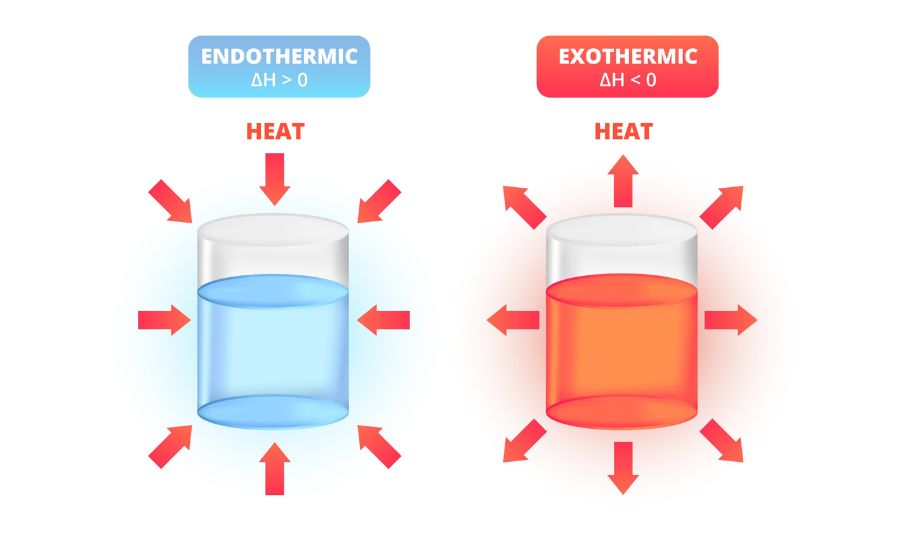
Before we dive into the specifics of popcorn popping, let’s clarify the concepts of endothermic and exothermic reactions.
- Endothermic Reactions: These reactions absorb energy from their surroundings. This means that the system, such as the popcorn kernels, takes in heat or other forms of energy, causing a temperature decrease in the surroundings. Examples of endothermic processes include melting ice or boiling water.
- Exothermic Reactions: In contrast, exothermic reactions release energy into their surroundings. This energy is usually in the form of heat, which increases the temperature around the system. Burning wood and fireworks are classic examples of exothermic reactions.
The Science of Popcorn Popping
To determine whether popcorn popping in a microwave oven is endothermic or exothermic, let’s explore the process in detail.
Microwave Oven Mechanism
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic radiation to heat food. These microwaves specifically target water molecules in the food, causing them to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, which cooks the food from the inside out.
Popcorn Kernels and Popping
Popcorn kernels are unique because they contain moisture inside a hard shell. When microwaved, the moisture inside each kernel heats up and turns into steam. As the steam builds up pressure, the kernel eventually bursts open, turning the starchy interior into the fluffy popcorn we enjoy.
Endothermic Nature of Popcorn Popping

The key to understanding whether this process is endothermic or exothermic lies in the energy exchange:
- Energy Absorption: When popcorn is placed in a microwave, it absorbs microwave radiation. This radiation is converted into heat energy, which raises the temperature of the kernels.
- Pressure Build-Up and Popping: As the temperature rises, the moisture inside the kernels turns into steam, building up pressure until the kernel bursts. This bursting releases energy in the form of steam and heat, but the initial process of heating up and popping the kernel requires energy absorption.
- Classification: The entire process starts with the absorption of energy (microwave radiation), making it an endothermic reaction. Although the popping of the kernel does release some energy, the primary phase where energy is absorbed makes it endothermic.
Comparing Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions in Popcorn Popping

To further clarify:
- Endothermic Aspect: The initial heating and energy absorption from the microwave radiation make popcorn popping an endothermic process. The energy is used to increase the temperature and pressure inside the kernels.
- Exothermic Aspect: Once the kernel pops, there is a release of energy in the form of heat and steam. However, this release is a minor part of the process compared to the energy absorbed initially.
Key Takeaway: Popcorn popping in a microwave oven is primarily an endothermic process due to the significant energy absorption required to heat the kernels and make them pop.
Real-World Implications and Applications
Understanding whether popcorn popping is endothermic or exothermic can have practical applications:
- Food Industry: The efficient heating of popcorn using microwaves demonstrates how endothermic processes are harnessed in everyday life, making snack preparation faster and more convenient.
- Thermal Dynamics Research: Studying how different materials, like popcorn kernels, absorb and release energy can provide insights into heat transfer and energy conversion, which is valuable in both scientific research and industrial applications.
FAQs
Q: Is a microwave oven endothermic or exothermic?
A: A microwave oven itself is not classified as endothermic or exothermic. However, the process of popping popcorn in a microwave oven is endothermic because the kernels absorb microwave radiation to generate heat.
Q: How does the endothermic process affect popcorn popping?
A: The endothermic process involves the absorption of energy (microwave radiation) by the popcorn kernels. This energy is converted into heat, which builds pressure inside the kernels and leads to the popping.
Q: Can you provide examples of endothermic and exothermic reactions other than popcorn popping?
A: Yes! Boiling water and melting ice are examples of endothermic reactions, while burning wood and fireworks are examples of exothermic reactions.
Q: Why is understanding endothermic and exothermic reactions important?
A: Knowing the difference between these reactions helps in understanding various processes in both scientific and everyday contexts, from cooking food to industrial applications.
Conclusion
In summary, the process of popcorn popping in a microwave oven is an endothermic reaction. The energy from the microwaves is absorbed by the popcorn kernels, causing them to heat up and eventually pop. While there is a release of energy when the kernels burst, the initial phase of energy absorption characterizes the process as endothermic. This distinction helps us appreciate the fascinating science behind one of our favorite snacks and highlights the broader principles of energy transfer in various contexts.
Feel free to share this article to spread the knowledge about the science behind popcorn popping, and stay tuned for more insights into everyday phenomena!
Read more: Mechpowerwashing
